Share
Surge Solutions
L-Carnitine Solution 500mg/ml
L-Carnitine Solution 500mg/ml
Couldn't load pickup availability
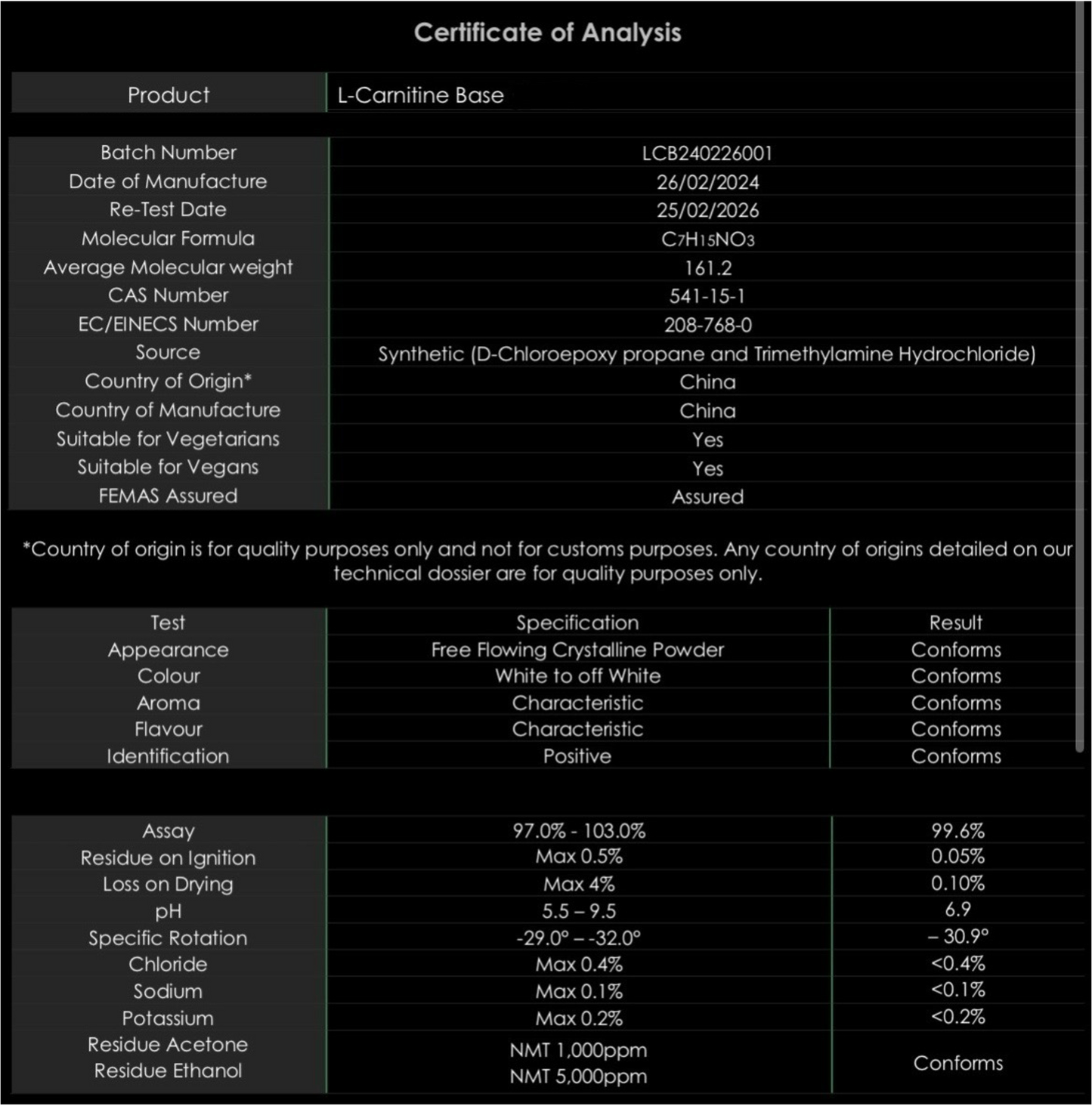
Our L-carnitine solution is made up of pure L-carnitine base powder (99%+ assay) mixed with distilled water- the gold standard of mixing water, free from heavy metals and other impurities.
The solution contains 0.9% benzyl alcohol to ensure long term sterility, and is filtered at 0.2 microns to remove any potential micro-organism contaminants, before being filled into our pressure-sterilised glass vials.
Rest assured, every measure is taken during production to provide our customers the purest product possible.
Sold for research use only.



deeper reading:
L-Carnitine for Natural Bodybuilding
TESTOSTERONE BOOSTING:
L-carnitine has a lot to offer for natural athletes who are aiming to build muscle and burn fat. Everybody understands the importance of testosterone in bodybuilding. Supplementing with L-carnitine is not only proven to increase endogenous production of testosterone and LH (1), but also to upregulate the activity and density of the androgen receptors in skeletal muscle tissue (2).
But what does this mean? Androgen receptors are responsible for binding to sex hormones from the bloodstream, and therefore determine the sensitivity of muscle cells to the anabolic effects of testosterone. Having high levels of androgens (testosterone) but poor androgen receptor activity is equivalent to having a kitchen full of ingredients, with no chefs to cook with them. Just as how many chefs and ingredients are needed to cook the maximum amount of food, high levels of androgens and androgen receptors are necessary to achieve the most efficient muscle growth.
NITRIC OXIDE INCREASE:
Separately from the hormonal benefits of L-carnitine supplementation, improved gym performance can aid natural bodybuilders in building muscle and burning energy more effectively. L-carnitine supplementation was shown in-study to increase endogenous production of nitric oxide (3), responsible for vasodilation and nutrient delivery. A full literature review on the effects of nitric oxide (4) find it to be significantly effective for improving strength adaptation, hypertrophy, and endurance-based performance. This mechanism of action is helpful for bodybuilders by promoting muscle nutrient delivery, increased gym workload, faster short-term recovery, and reduced muscle soreness.
INCREASED FAT OXIDATION:
L-carnitine plays a crucial role in transporting long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondria, where they are oxidized to produce energy (5). By enhancing this process, L-carnitine helps increase the body's ability to utilize fat as a fuel source, particularly during exercise. For natural bodybuilders, this means more efficient fat burning in 2 main applications:
1. During fasted cardio, supplementing L-carnitine will allow for a higher intensity of work to be done, due to more energy being synthesised from free fatty acids. This will aid the athlete in feeling less lethargic, risking less muscle loss, and improving overall performance during these sessions.
2. During normal training, carnitine supplementation will allow for muscle glycogen stores to be preserved, and fat burning to be biased. Not only does this offer benefits for body composition, it also allows longer work sessions can be completed due to reduced carbohydrate depletion, as well as reduced build up of lactic acid and hydrogen ions in muscle tissue (6).
REFERENCES:
1. Ma, L., & Sun, Y. (2022). Comparison of L-Carnitine vs. Coq10 and Vitamin E for idiopathic male infertility: a randomized controlled trial. European review for medical and pharmacological sciences, 26(13), 4698–4704. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202207_29194
2. Kraemer, W. J., Spiering, B. A., Volek, J. S., Ratamess, N. A., Sharman, M. J., Rubin, M. R., French, D. N., Silvestre, R., Hatfield, D. L., Van Heest, J. L., Vingren, J. L., Judelson, D. A., Deschenes, M. R., & Maresh, C. M. (2006). Androgenic responses to resistance exercise: effects of feeding and L-carnitine. Medicine and science in sports and exercise, 38(7), 1288–1296. https://doi.org/10.1249/01.mss.0000227314.85728.35
3. Atalay Guzel, N., Erikoglu Orer, G., Sezen Bircan, F., & Coskun Cevher, S. (2015). Effects of acute L-carnitine supplementation on nitric oxide production and oxidative stress after exhaustive exercise in young soccer players. The Journal of sports medicine and physical fitness, 55(1-2), 9–15. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25289711/
4. Gonzalez AM, Townsend JR, Pinzone AG, Hoffman JR. Supplementation with Nitric Oxide Precursors for Strength Performance: A Review of the Current Literature. Nutrients. 2023 Jan 28;15(3):660. doi: 10.3390/nu15030660. PMID: 36771366; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9921013/
5. Virmani MA, Cirulli M. The Role of l-Carnitine in Mitochondria, Prevention of Metabolic Inflexibility and Disease Initiation. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 28;23(5):2717. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052717. PMID: 35269860; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8910660/
6. Wall, B. T., Stephens, F. B., Constantin-Teodosiu, D., Marimuthu, K., Macdonald, I. A., & Greenhaff, P. L. (2011). Chronic oral ingestion of L-carnitine and carbohydrate increases muscle carnitine content and alters muscle fuel metabolism during exercise in humans. The Journal of physiology, 589(Pt 4), 963–973. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2010.201343
L-Carnitine for Enhanced Bodybuilding
ANDROGEN RECEPTOR ACTIVITY:
L-carnitine supplementation is proven to aid enhanced athletes to get the most out of their AAS via androgen receptor (AR) synergy. Elevated muscle-carnitine levels has been found (1) to increase the translocation speed and binding affinity of androgen receptors, as well as muscle AR density. With enhanced athletes, the levels of androgens in the bloodstream is not going to be a limiting factor to hypertrophy, so improving the muscle's ability to use these hormones for anabolic effect is a strong approach to accelerate hypertrophy without increasing oxidative and organ stress.
IMPROVED NUTRIENT PARTITIONING:
L-carnitine plays a crucial role in transporting long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondria, where they are oxidized to produce energy (2). By enhancing this process, L-carnitine helps increase the body's ability to utilize fat as a fuel source, particularly during exercise. This gives advantage to an athlete in multiple dimensions, such as:
-Increased muscle-glycogen retention and continuous fat loss during aggressive fat-loss phases such as contest prep (3)
-Reduced fat gain and biased muscle accumulation during a massing phase (4)
-Reduced lethargy, appetite and cravings during a fat-loss phase due to steadier energy supply from free fatty acid oxidation (5)
PUMP, ENDURANCE AND NUTRIENT DELIVERY:
L-carnitine supplementation was shown in-study to increase endogenous production of nitric oxide (6), responsible for vasodilation and nutrient delivery. This vasodilation effect often also increases vascular appearance in lean athletes due to widened and more surfaced blood vessels. In addition, increased nutrient delivery is speculated to be a significant anabolic driver in enhanced athletes (7), hence the use of insulin in bodybuilding.
The vasodilation effects of L-carnitine via nitric oxide production also provides users an increase in endurance, by heightening maximum fat-oxidation threshold (FATMAX) (8). This bias of fat-burning and consequent decrease in glucose oxidation reduces byproducts lactate and hydrogen, which are proven to inhibit ability to contract muscle tissue. The reduction in muscle acidosis allows users to train for longer durations at high intensity, and require shortened recovery periods (9).
REFERENCES:
1. Kraemer, W. J., Spiering, B. A., Volek, J. S., Ratamess, N. A., Sharman, M. J., Rubin, M. R., French, D. N., Silvestre, R., Hatfield, D. L., Van Heest, J. L., Vingren, J. L., Judelson, D. A., Deschenes, M. R., & Maresh, C. M. (2006). Androgenic responses to resistance exercise: effects of feeding and L-carnitine. Medicine and science in sports and exercise, 38(7), 1288–1296. https://doi.org/10.1249/01.mss.0000227314.85728.35
2. Virmani MA, Cirulli M. The Role of l-Carnitine in Mitochondria, Prevention of Metabolic Inflexibility and Disease Initiation. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 28;23(5):2717. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052717. PMID: 35269860; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8910660/
3. Ling-Yu Li, Dong-Liang Lu, Zhe-Yue Jiang, Samwel Mchele Limbu, Fang Qiao, Li-Qiao Chen, Mei-Ling Zhang, Zhen-Yu Du (2020) Dietary L-carnitine improves glycogen and protein accumulation in Nile tilapia via increasing lipid-sourced energy supply: An isotope-based metabolic tracking. School of Life Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2020.100302
4. Talenezhad, N., Mohammadi, M., Ramezani-Jolfaie, N., Mozaffari-Khosravi, H., & Salehi-Abargouei, A. (2020). Effects of l-carnitine supplementation on weight loss and body composition: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 37 randomized controlled clinical trials with dose-response analysis. Clinical nutrition ESPEN, 37, 9–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.03.008
5. Zhang, Jj., Wu, Zb., Cai, Yj. et al. L-carnitine ameliorated fasting-induced fatigue, hunger, and metabolic abnormalities in patients with metabolic syndrome: a randomized controlled study. Nutr J 13, 110 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-13-110
6. Atalay Guzel, N., Erikoglu Orer, G., Sezen Bircan, F., & Coskun Cevher, S. (2015). Effects of acute L-carnitine supplementation on nitric oxide production and oxidative stress after exhaustive exercise in young soccer players. The Journal of sports medicine and physical fitness, 55(1-2), 9–15. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25289711/
7. de Freitas, M. C., Gerosa-Neto, J., Zanchi, N. E., Lira, F. S., & Rossi, F. E. (2017). Role of metabolic stress for enhancing muscle adaptations: Practical applications. World journal of methodology, 7(2), 46–54. https://doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v7.i2.46
8. Wall, B. T., Stephens, F. B., Constantin-Teodosiu, D., Marimuthu, K., Macdonald, I. A., & Greenhaff, P. L. (2011). Chronic oral ingestion of L-carnitine and carbohydrate increases muscle carnitine content and alters muscle fuel metabolism during exercise in humans. The Journal of physiology, 589(Pt 4), 963–973. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2010.201343
9. Stefan, M., Sharp, M., Gheith, R., Lowery, R., Ottinger, C., Wilson, J., Durkee, S., & Bellamine, A. (2021). L-Carnitine Tartrate Supplementation for 5 Weeks Improves Exercise Recovery in Men and Women: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients, 13(10), 3432. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103432.




